SURGICAL PROCEDURES
NAD+
NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. It plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes, including energy production, DNA repair, and cellular signaling.

- Energy Metabolism: NAD+ is a key player in cellular respiration, which is the process by which cells convert nutrients into energy. It acts as a coenzyme in both glycolysis (the breakdown of glucose) and the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle), facilitating the transfer of electrons and the production of ATP, the cell's primary energy currency.
- DNA Repair: NAD+ is involved in DNA repair mechanisms, specifically in processes like base excision repair and DNA strand break repair. These mechanisms help maintain genomic stability and prevent mutations that could lead to diseases such as cancer.
- Cellular Signaling: NAD+ also acts as a substrate for various enzymes called sirtuins, which play critical roles in regulating cellular processes such as gene expression, apoptosis (programmed cell death), and stress responses. Sirtuins are involved in longevity and have been linked to the health benefits of caloric restriction and exercise.
- Redox Reactions: NAD+ participates in redox reactions by accepting and donating electrons. It exists in two forms: oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (NADH). During cellular respiration, NAD+ is reduced to NADH by accepting electrons from metabolic intermediates, and then NADH is oxidized back to NAD+ in the electron transport chain, generating ATP.
Overall, NAD+ is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating various physiological processes, making it a crucial molecule for overall health and vitality. Its levels can be influenced by factors such as diet, exercise, and aging, and there is growing interest in NAD+ supplementation as a potential therapeutic intervention for age-related diseases and metabolic disorders.
RF Needling Scarlet
A new innovative, safe, and effective procedure has recently gained popularity in the local cosmetic and plastic surgery market here. Scarlet MFR provides women with painless, non-surgical facelifts.
“Scarlet MFR is a new generation of skin rejuvenation technology that utilizes Microneedle Fractional Radiofrequency (MFR) rather than laser,” “Scarlet not only builds up collagen to tighten up the skin, but also improves dermal volume and elastin to improve skin elasticity, texture and turgor resulting in perceptible skin improvement.
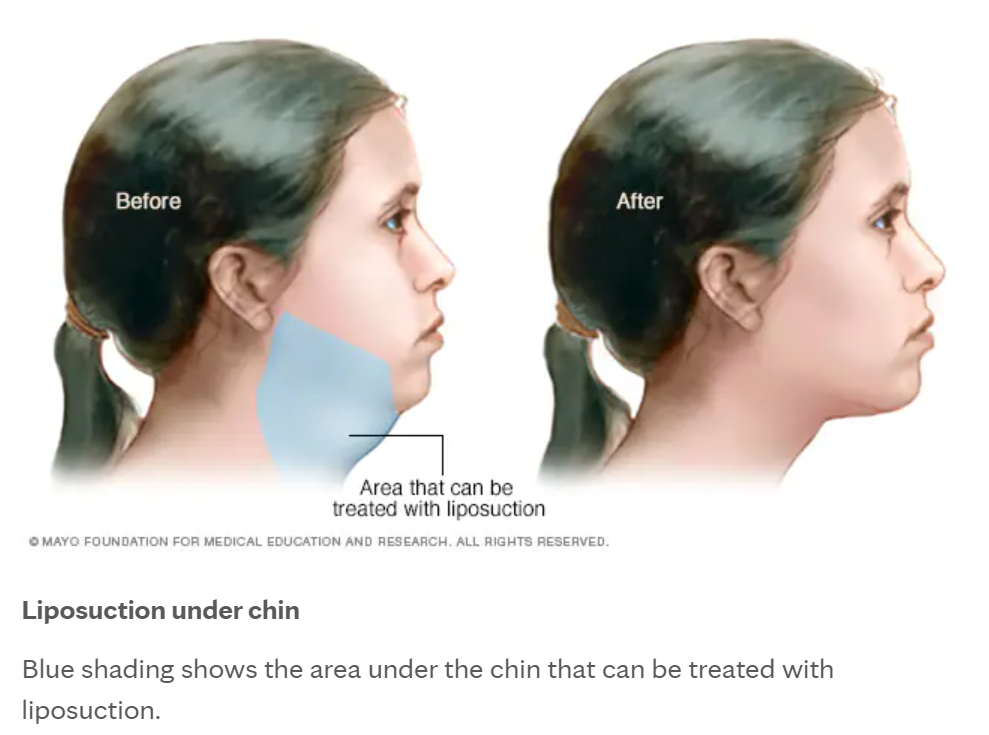
Liposuction
Liposuction is a type of surgery. It uses suction to remove fat from specific areas of the body, such as the stomach, hips, thighs, buttocks, arms or neck. When you gain weight, fat cells get bigger. Liposuction lowers the number of fat cells in a specific area. The amount of fat removed depends on what the area looks like and the volume of fat. The resulting shape changes are usually permanent as long as your weight remains the same. Liposuction may work for you if you have a lot of body fat in specific places but otherwise have a stable body weight.
After liposuction, the skin molds itself to the new shapes of the treated areas. If you have good skin tone and elasticity, the skin usually looks smooth.
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton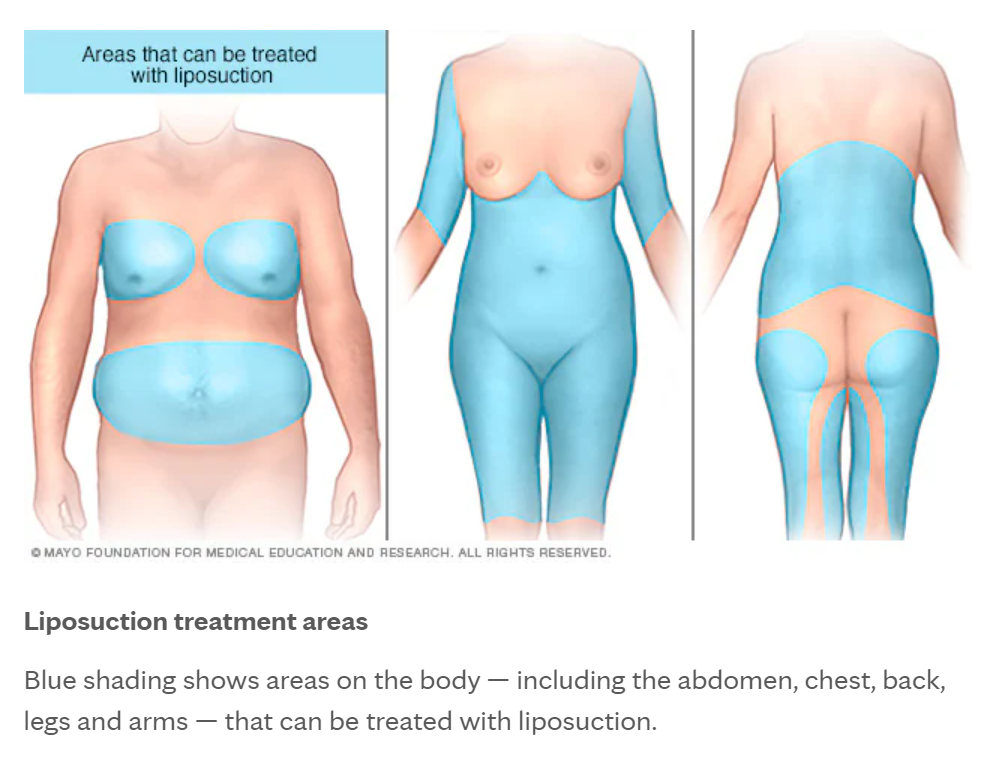
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Fat Grafting (Fat Transferring)
Fat grafting, also referred to as fat transfer or fat injections, is the surgical process by which fat is transferred from one area of the body to another area. The surgical goal is to improve or augment
the area where the fat is injected. The technique involves extracting adipose fat by liposuction, processing the fat and then reinjecting purified fat into the area needing improvement.
Fat Grafting Process
The process of fat grafting involves three steps:
- Extraction of the fat from the donor area with liposuction
- Decanting, centrifugation and processing of the fat
- Reinjection of the purified fat into the area needing improvement
Business Hours
- Mon - Sun
- -
WeChat ID: Rosemila2010







